The Union Budget for the fiscal year 2024-2025 has been announced, presenting a detailed and ambitious roadmap towards the vision of a ‘Viksit Bharat‘ or a developed India. This budget is designed with a focus on inclusivity, sustainability, and robust economic growth. The key features of this budget encompass various sectors, aiming to enhance productivity, resilience, and social justice across the country.
Employment and Skilling
Facilitating Women’s Participation
To boost women’s participation in the workforce, the budget has allocated funds for setting up working women’s hostels and establishing crèches in collaboration with the industry. This initiative aims to create a supportive environment for women, allowing them to balance work and family life effectively.
Wage Support for New Entrants
The budget includes a provision of a one-month wage to new entrants in all formal sectors in three instalments, up to ₹15,000. This initiative is expected to benefit 210 lakh youth, encouraging fresh talent to join the workforce.
EPFO Contribution Incentives
Under Scheme A, both employees and employers will receive incentives for EPFO contributions for the first four years of employment. This scheme is expected to benefit 30 lakh youth, providing them with financial stability and social security.
Job Creation in Manufacturing
Scheme B focuses on job creation in the manufacturing sector, while Scheme C offers support to employers by reimbursing EPFO contributions up to ₹3000 per month for two years for all new hires. These schemes are expected to generate 50 lakh jobs, significantly boosting employment in the country.
Education and Skilling Programs
The budget also emphasises education and skilling programs, with financial support for loans up to ₹10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions. Direct e-vouchers will be provided to 1 lakh students annually, along with an annual interest subvention of 3%. Additionally, 20 lakh youth will be skilled over a five-year period, and 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes will be upgraded to align with industry needs.
Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
Purvodaya: Vikas bhi Virasat bhi
The Purvodaya initiative aims to develop the Eastern states of Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh by generating economic opportunities and preserving cultural heritage. This includes the development of the Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor with an industrial node at Gaya.
Women and Girls Empowerment
Over ₹3 lakh crore has been allocated for schemes benefiting women and girls, focusing on improving their socio-economic conditions and providing them with better opportunities.
Tribal Development
The Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan aims to improve the socio-economic condition of tribal communities, covering 63,000 villages and benefiting 5 crore tribal people. More than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank will be set up in the North East region to facilitate financial inclusion.
Manufacturing and Services
Industrial Parks and Internship Opportunities
Twelve industrial parks will be developed under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme, creating numerous employment opportunities. Additionally, a scheme for providing internship opportunities in 500 top companies to 1 crore youth over five years has been introduced, offering an allowance of ₹5,000 per month along with a one-time assistance of ₹6,000 through CSR funds.
Rental Housing and Credit Support
The budget also includes provisions for rental housing with dormitory-type accommodation for industrial workers in a PPP mode with VGF support. Furthermore, credit support to MSMEs during stress periods and an enhanced scope for mandatory onboarding in TReDS are highlighted, along with a new assessment model for MSME credit.
Urban Development and Energy Security
Stamp Duty and Urban Planning
States are encouraged to lower stamp duties for properties purchased by women, promoting home ownership among women. The budget envisions a scheme to develop 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs in select cities and transit-oriented development plans for 14 large cities with a population above 30 lakh.
Housing and Infrastructure
The PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0 aims to address the housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families with an investment of ₹10 lakh crore. Enabling policies and regulations for efficient and transparent rental housing markets will also be put in place.
Energy Initiatives
The budget outlines several energy initiatives, including the setting up of Bharat Small Reactors, R&D of Bharat Small Modular Reactor, and new technologies for nuclear energy. Financial support will be provided for shifting micro and small industries to cleaner forms of energy, and a joint venture between NTPC and BHEL will set up a full-scale 800 MW commercial plant.
Infrastructure Development
Long-term Interest-free Loans to States
A provision of ₹1.5 lakh crore in long-term interest-free loans to states has been made to support resource allocation and infrastructure development. Phase IV of PMGSY will be launched to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations, and financial support for projects such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and other ongoing and new schemes will be provided.
Flood Management and Reconstruction
The budget also includes assistance for flood management and related projects in Assam, Sikkim, and Uttarakhand, as well as for reconstruction and rehabilitation in Himachal Pradesh.
Innovation, Research & Development
National Research Fund
The operationalization of the Anusandhan National Research Fund for basic research and prototype development is a key highlight. A private sector-driven research and innovation initiative with a financing pool of ₹1 lakh crore is also proposed, along with the establishment of a venture capital fund of ₹1,000 crore for the space economy.
Tax Proposals
Simplification and Relief
The budget proposes simplification in taxes and a comprehensive review of the Income Tax Act 1961. Several changes in customs duty have been announced to boost strategic sectors and enhance competitiveness in marine exports. The tax regime for domestic cruise operations will be simplified, and a safe harbour rate for foreign mining companies selling raw diamonds will be provided. The corporate tax rate on foreign companies will be reduced from 40% to 35%.
Capital Gains and Exemptions
Short-term gains on financial assets will attract a 20% tax rate, while long-term gains on all financial and non-financial assets will attract a tax rate of 12.5%. The limit of exemption on capital gains on financial assets will be increased to ₹1.25 lakh per year.

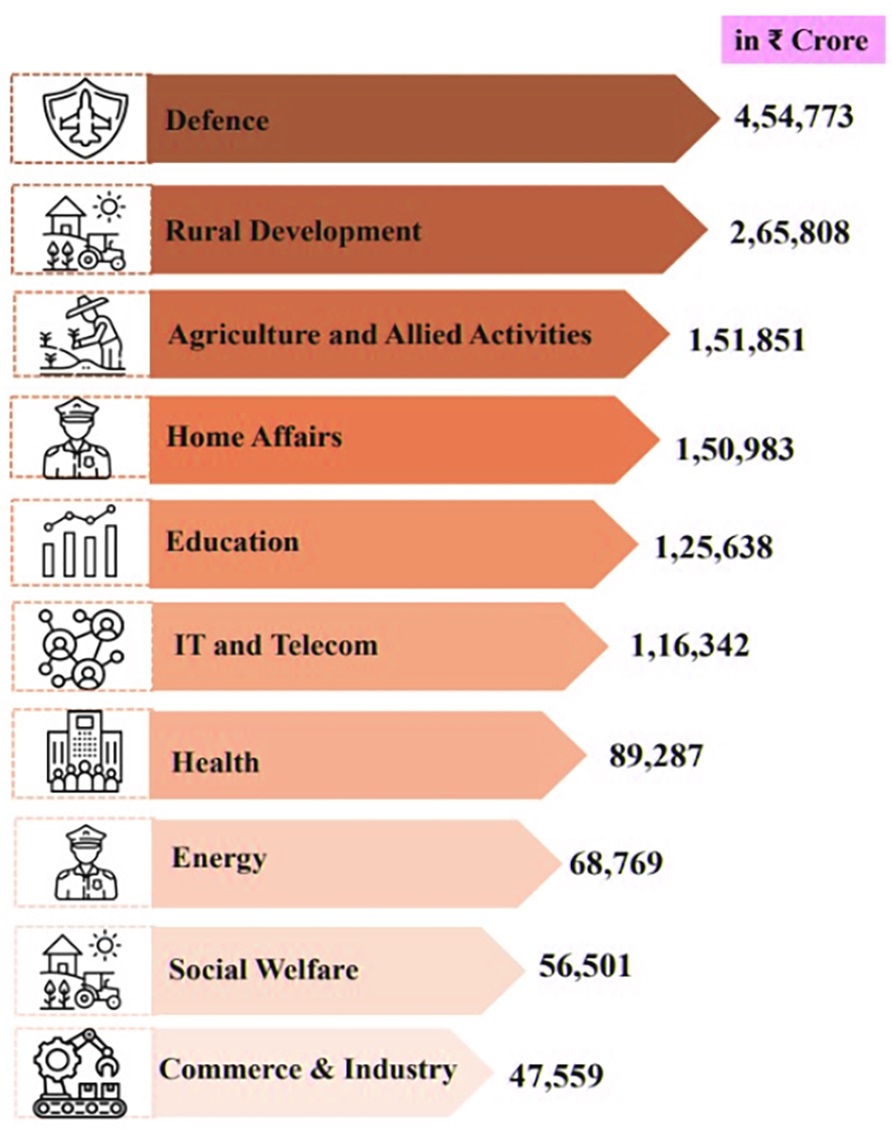
Expenditure on Major Items:
Conclusion
The Union Budget 2024-2025 lays out a comprehensive plan for achieving a Viksit Bharat by addressing key areas such as employment, skilling, social justice, manufacturing, urban development, energy security, infrastructure, innovation, and tax simplification. By focusing on inclusive growth and sustainability, this budget aims to propel India towards becoming a developed nation, ensuring prosperity and well-being for all its citizens.




