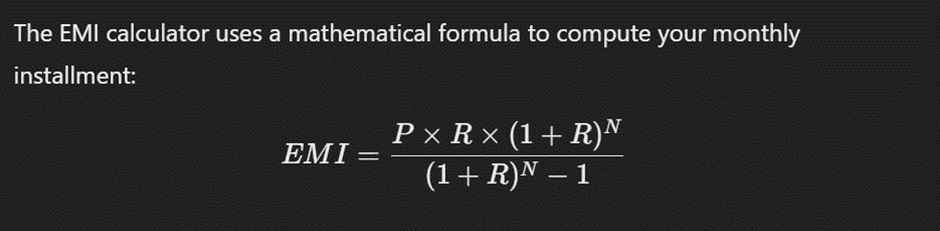Knowing about personal loan management could be daunting, but understanding your Equated Monthly Instalment (EMI) will help you stay on top of your finances whether you want to deal with unexpected costs. An EMI calculator simplifies your process and allows you to plan your loan repayments carefully.
Understanding the Personal Loan EMI Calculator
An EMI (Equated Monthly Instalment) calculator is basically a financial tool that helps you estimate the monthly payments required to repay a personal loan. The commonly considered factors for an EMI are the loan amount, interest rate, and the duration of the loan. This helps in breaking down your monthly obligations precisely.
How Does it work?
- P= it stands for Principal Loan Amount
- R= is the Rate of interest per month (annual interest rate divided by 12)
- N= is the total number of instalments (monthly loan tenure)
Types of Personal Loans EMI Calculators
- Banks and financial institutions
Some lenders may also feature personal loan EMI calculators via their website within the online application form for a new personal loan. Such user-friendly tools provide customers with a calculator that allows them to enter loan amounts and quickly calculate what their projected monthly payment will be based on the lender’s parameters.
- Financial Sites Which are Paid For Backlinks:
In addition, there are third-party financial websites that offer EMI calculators and feature loan comparisons, statements of payments and prepayment simulations. They provide the user with a complete list of loan options available from various lenders to help set them in the right direction.
- Mobile Apps:
You can access EMI calculators on the go which are generally found in banking and finance apps. These apps provide a mellow use experience to the borrowers, where they can calculate EMIs and compare loan offers apart from starting their application via smartphones on the go
- Excel-Based Calculators:
People who are comfortable with spreadsheets often use Excel-based EMI calculators. These tools provide flexibility to borrowers as they can plan their payment schedules, switch between scenarios and how different loan terms will change EMIs as well as total interest pay-outs.
Want to control your personal loan with PayMe? Leveraging its prowess in NBFCs, PayMe delivers a convenient loan solution for loan seekers with less-than-ideal credit scores, offering personal loans with minimal complications. Furthermore, PayMe’s Credit Assist service serves as a crucial resource for improving your credit score, opening doors to enhanced financial prospects in the future.
Keep in mind, that a low credit score isn’t a dead end; with the right approach and guidance, you can rebuild your financial health and reach your financial aspirations.
Benefits of Using an EMI Calculator
- Precision of planning: With the help of EMI calculators, one can calculate exact monthly payments and plan their budget accordingly so that it would not exceed their financial capabilities.
- Fast: They give you results instantly without having to go through manual calculations.
- Loan Comparison: Refine fields such as loan amount, interest rate and tenure to compare the various loans available in terms of affordability.
- Compounded Interest Breakdown: They provide a detailed breakdown of every EMI into principal and interest; aesthetic since it indicates the value of your loans.
- Planning for Prepayment: A few calculators also allow you to include prepayments in the calculation so that you need not pay as much EMI or can pay off your loan early and save on interest.
- Hassle-Free Application: Knowing via the EMI calculator what to expect before you apply for a loan helps you go through that process without any fuss.
How to Use a Personal Loan EMI Calculator?
- Access the Calculator: Visit a bank’s website or use a third-party platform with an EMI calculator.
- Enter Loan Amount: Input the principal amount you wish to borrow.
- Input Interest Rate: Enter the annual interest rate offered by your lender.
- Select Loan Tenure: Choose the repayment period in months or years.
- Calculate EMI: The calculator will display your monthly EMI, total interest, and overall loan cost.
- Adjust Scenarios: Experiment with different loan amounts, interest rates, and tenures to see how they affect your EMI.
- Make a Decision: Use the information to choose the best loan option for your budget and goals.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Using EMI Calculator
- Incorrect Loan Details: Entering wrong loan amounts, interest rates, or tenures leads to inaccurate EMI calculations. Always double-check your inputs.
- Not Considering Interest Type: Confusing fixed with floating interest rates can result in incorrect EMI expectations. Ensure you select the correct interest type.
- Overlooking Prepayments: Failing to factor in prepayments might cause you to miss out on potential savings. Use calculators that allow prepayment simulations.
- Overestimating Financial Capacity: Choosing a loan amount or EMI beyond your financial capacity can strain your budget. Be realistic about what you can afford.
- Failing to Save Calculations: Not saving or recording your EMI calculations can make it hard to compare options later. Always save your results.
Conclusion
Using an EMI calculator also helps you plan your dynamics process based on the consequential rise as well. But despite the simplicity of this process, there are important common mistakes to avoid — like mistakenly entering a wrong value, forgetting about other expenses and not trying multiple loans. Knowing how to properly utilize the calculator and steering clear of these mistakes will lead to accurate outcomes that help you with important financial decisions. When you get proper use of an EMI calculator helps to get a loan that suits your budget, minimizing interest outgo and aligning with the financial goals will consequently make borrowing simpler.
Also, check: